Brownian Crystallisation (Diffusion-Limited Aggregation)
Stochastic simulation of crystallisation via Brownian motion and irreversible aggregation.
Overview
This project investigates Brownian crystallisation using a diffusion-limited aggregation (DLA) model. Particles undergo random walks on a two-dimensional lattice and irreversibly bind upon contact with a growing solid cluster, forming emergent crystalline and fractal structures.
The simulation explores how simple stochastic rules at the microscopic level lead to complex macroscopic structure — a central theme in statistical physics and non-equilibrium systems.
Physical Model
- Particles perform discrete two-dimensional Brownian motion
- Motion occurs on a finite square lattice
- Particles stick irreversibly upon first contact with the aggregate
- The aggregate acts as a growing absorbing boundary
This model captures the essential physics of crystallisation and pattern formation in diffusion-dominated regimes, relevant to crystal growth, electrochemical deposition, and colloidal aggregation.
Implementation
- Monte Carlo simulation of multi-particle random walks
- Vectorized NumPy operations for efficient state updates
- Explicit tracking of particle trajectories and aggregate geometry
- Frame-by-frame visualization and animation generation
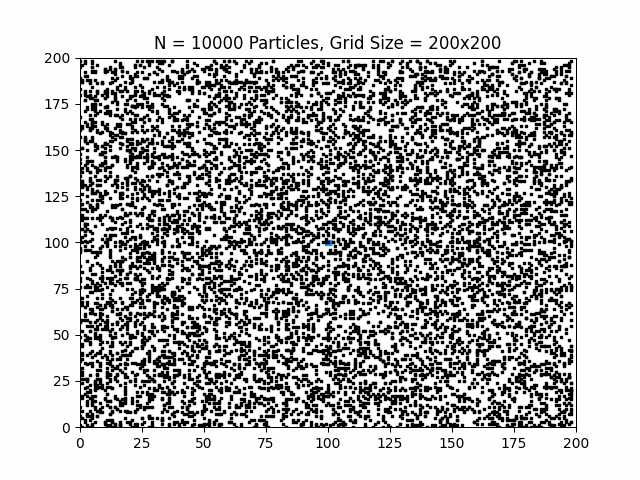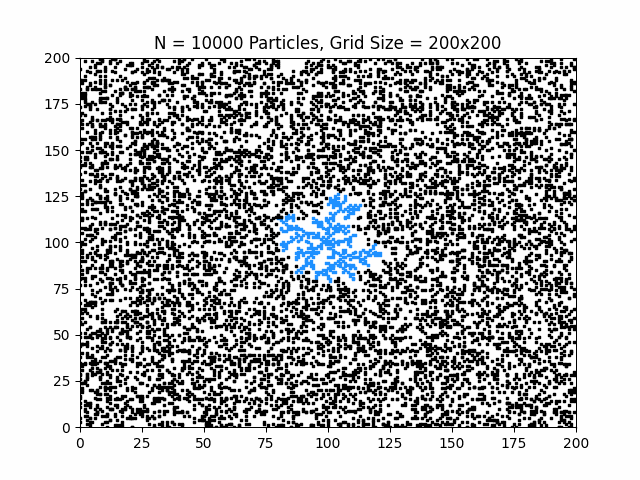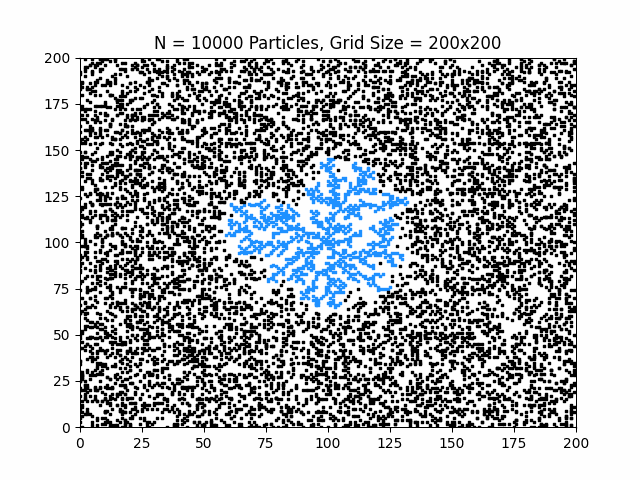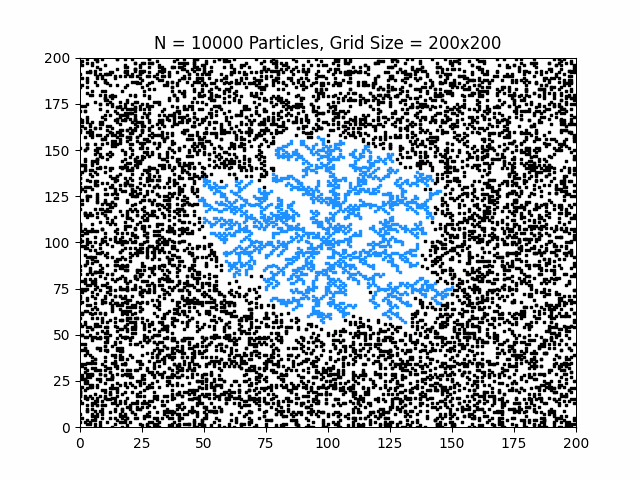
The animation above shows particles diffusing through the lattice and progressively attaching to the growing crystal, revealing the characteristic branching morphology of diffusion-limited growth.
Key Observations
- Growth is highly anisotropic despite isotropic diffusion
- Branching structures emerge naturally from stochastic motion
- Aggregate morphology depends sensitively on particle density and lattice size
- The resulting crystal exhibits fractal-like geometry
Why This Matters
Diffusion-limited aggregation provides a minimal yet powerful framework for understanding non-equilibrium structure formation. Variants of this model appear in:
- Crystal growth and solidification
- Electrodeposition and corrosion
- Colloidal physics and soft matter
- Pattern formation in biological systems
This project emphasizes how physically meaningful behavior can emerge from simple probabilistic rules — a recurring theme across physics, materials science, and complex systems.
Tools & Techniques
- Python
- NumPy
- Matplotlib
- Monte Carlo methods
- Stochastic simulation